Interpreting Historical Maps: A Guide for Researchers
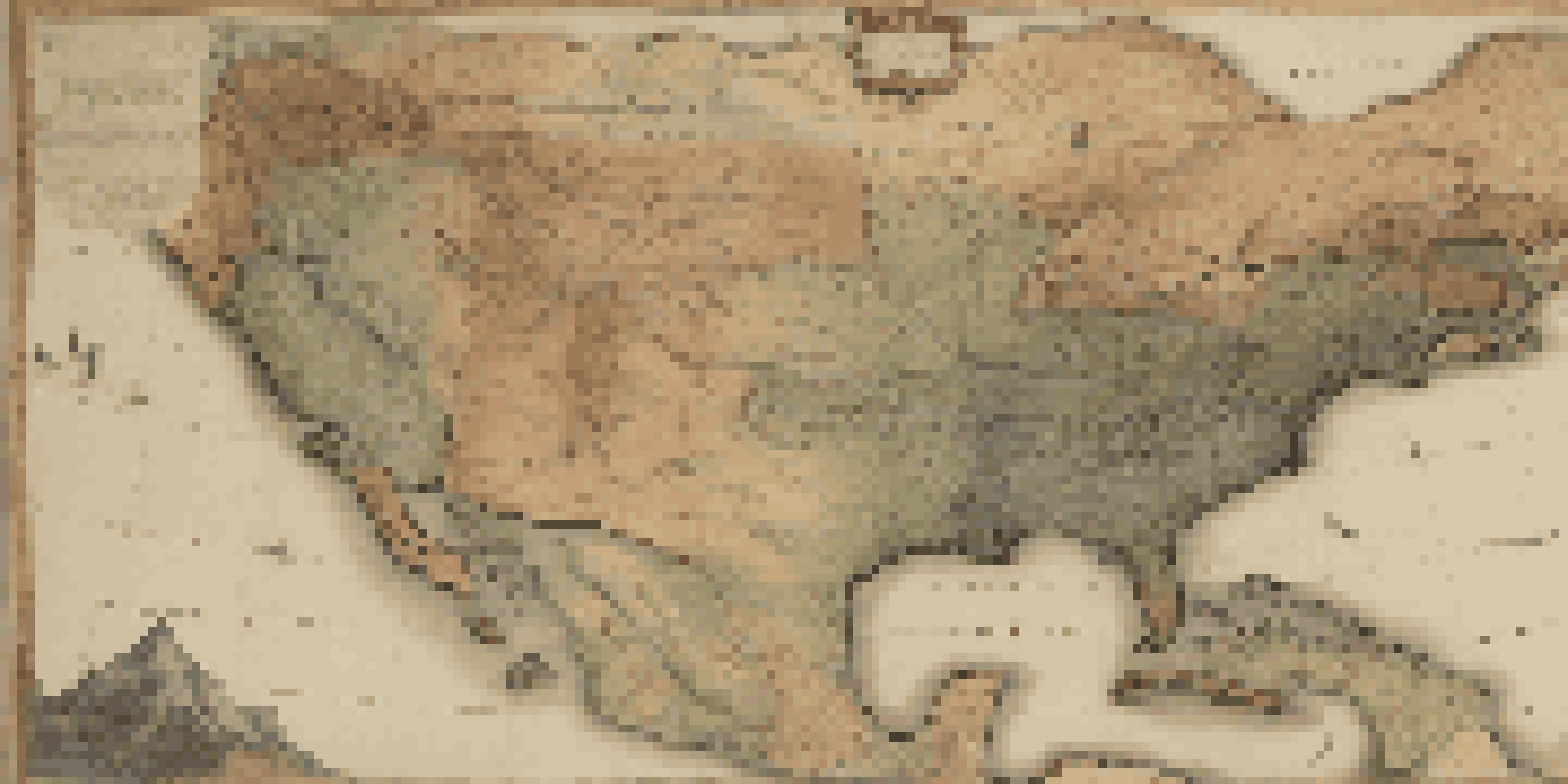
Understanding the Significance of Historical Maps
Historical maps are not just relics of the past; they are windows into how people viewed their world at different times. They can reveal insights about geography, political boundaries, and even social hierarchies. By understanding the significance of these maps, researchers can uncover stories that may have been forgotten or overlooked.
Maps are a way of organizing wonder.
For instance, a map from the early 1800s might show territorial claims that have since changed, illustrating the shifting nature of power and influence. These documents serve as time capsules that can help us understand historical events more deeply. Therefore, recognizing their importance is the first step in interpreting them effectively.
Additionally, historical maps can also reflect cultural perspectives. The way a place is depicted can vary significantly based on the mapmaker’s background, intentions, and the audience they were targeting. This cultural lens can influence everything from the geographic details included to the symbolic elements represented.
Types of Historical Maps and Their Uses
There are several types of historical maps, each serving unique purposes. Topographic maps, for example, focus on the physical landscape, showing elevation and terrain features. On the other hand, political maps highlight boundaries and territorial divisions, often reflecting the political climate of their time.
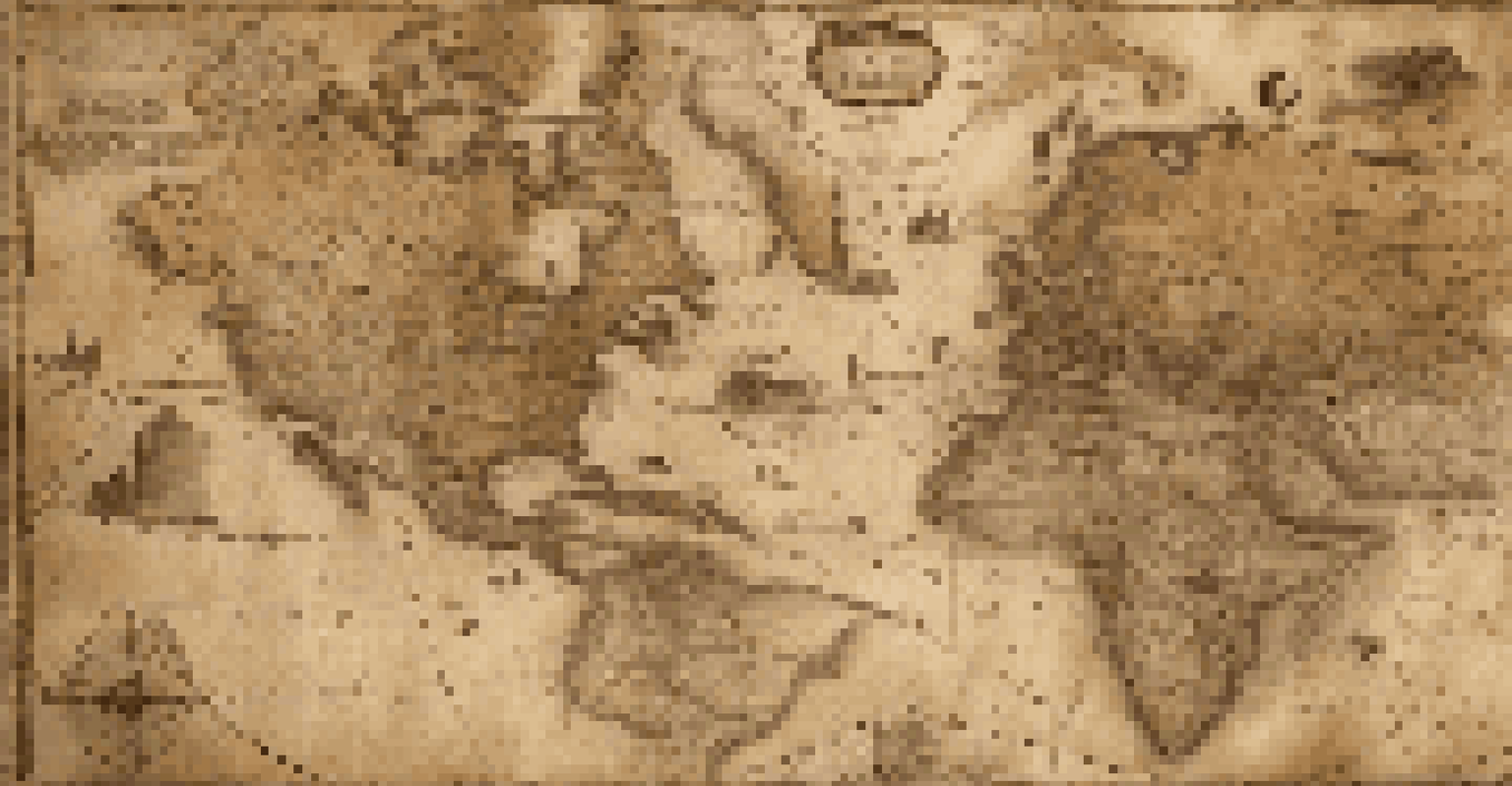

The style and content of a map can also vary widely depending on the era. Maps from the Renaissance period, for instance, often included artistic elements to beautify the representation of the world, while 20th-century maps may prioritize accuracy and scientific data. Understanding these types helps researchers choose the right map for their specific inquiry.
Historical Maps as Cultural Insights
Historical maps reveal not only geographical details but also cultural perspectives and societal hierarchies of their time.
Moreover, thematic maps present information on specific topics, such as population density or economic activity. These maps can be particularly useful for researchers focusing on social sciences, as they highlight trends and changes over time, making it easier to draw connections between geography and societal developments.
Decoding Map Symbols and Legend
Every historical map comes with a set of symbols and a legend that provide crucial context. Decoding these symbols is essential for understanding what the map is trying to convey. For instance, a simple line might represent a river, while colored areas could indicate different land uses or political regions.
The map is not the territory.
Take the time to study the legend closely, as it will often contain information on the map's scale and the time period it represents. This context is vital because it allows you to interpret the data accurately. Without understanding the symbols, you risk missing out on important details that could alter your research findings.
Additionally, some historical maps may feature unique symbols that were specific to the mapmaker’s style or the conventions of their time. Learning to recognize these idiosyncrasies can give you deeper insights into the intentions behind the map and the historical context it was created in.
Evaluating the Accuracy of Historical Maps
When working with historical maps, it's crucial to assess their accuracy. Maps from earlier periods often reflect the limited knowledge of the world at that time. For example, a map from the 1600s might depict a continent's coastline inaccurately due to the lack of detailed exploration.
To evaluate a map's accuracy, researchers can compare it with modern maps and geographical data. This process can reveal discrepancies and help contextualize the information presented. It's a bit like piecing together a puzzle; each map can provide valuable clues about the world as it was understood in the past.
Evaluating Map Accuracy is Essential
Assessing the accuracy of historical maps involves comparing them with modern data and understanding their sources.
Moreover, consider the sources used to create the map. Maps based on firsthand exploration may be more reliable than those created from hearsay. Understanding the origins of the map can inform your evaluation of its accuracy and relevance to your research.
Contextualizing Historical Maps in Time and Space
Context is everything when interpreting historical maps. The time period in which a map was created can greatly influence its content and perspective. For instance, a map created during a time of conflict might emphasize military routes and strategic locations, reflecting the priorities of that era.
Similarly, the geographical context matters too. A map of a region undergoing rapid industrialization will look different from one depicting the same area a century earlier. Understanding these changes allows researchers to appreciate the evolution of a geographical space over time.
By situating a map within its historical and geographical context, researchers can draw more nuanced conclusions about the events and dynamics at play. This broader perspective enriches the analysis and provides a deeper understanding of how societies interacted with their environments.
Utilizing Technology for Map Analysis
In today’s digital age, technology plays a significant role in historical map analysis. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow researchers to overlay historical maps with modern data, revealing patterns that may not be immediately obvious. This technological integration can breathe new life into old maps, making them even more valuable for contemporary research.
Moreover, online archives and databases have made it easier than ever to access a wide range of historical maps from around the world. Many institutions digitize their collections, providing researchers with tools to analyze and compare maps from various sources, all from the comfort of their own homes.
Technology Enhances Map Analysis
Modern tools like GIS and online archives significantly improve the analysis and accessibility of historical maps for researchers.
Utilizing these technological resources not only facilitates the research process but also encourages collaboration among historians, geographers, and other professionals. By sharing insights and findings through digital platforms, the academic community can contribute to a richer, more comprehensive understanding of historical geography.
Practical Tips for Researchers Using Historical Maps
When diving into the world of historical maps, a few practical tips can enhance your research experience. Start by clearly defining your research question, as this will guide your selection of maps and data. Having a focused inquiry helps streamline the process and makes it easier to identify relevant resources.
Next, take detailed notes as you analyze each map. Documenting your observations about symbols, context, and accuracy will make it easier to synthesize your findings later. This practice also aids in drawing connections between various maps and the historical narratives they represent.
Finally, don’t hesitate to consult with experts or join online forums dedicated to historical geography. Engaging with a community of fellow researchers can provide valuable insights and open up new avenues for exploration. Remember, the journey of interpreting historical maps can be as enriching as the discoveries you make along the way.